The December 2025 Google Core Update Is Complete: What Does It All Mean?
When a Google core update is being rolled out, digital marketers everywhere eagerly wait to…
Back in 2012, Google launched an algorithm update which was intended to target webspam in particular. Namely, this would focus on link spam and manipulative link buildingLink building is a process of acquiring links pointing to your website. These links are obtained by creating content, participating in social media or commenting on other blogs. which specific individuals or businesses may use, such as cramming their keywords into almost all of the sentences on a page or seeking an extensive number of backlinks from unworthy sites. This update was the Google Penguin Algorithm Update.
As part of Google’s never ending battle to provide the most relevant and top-quality content on its results pages, an effort which b2b SEO strategy experts can sympathise with, this update came at a time when it appeared that low-quality websites were being ranked higher than organically relevant pages, simply due to the number of linksHyperlinks, also known as links, are the connection points on a webpage that take you to other webpages. included on the site. This came at a time when, before the Penguin Update, Google reacted more positively to a higher amount of links when analysing and indexing page content.
Therefore, many low-quality websites which had stuffed content with a high number of links were beginning to be ranked higher than more relevant results; poor news for hardworking businesses and their SEO b2b and general SEO. Google couldn’t allow this; therefore, the Penguin Algorithm Update was rolled out to tackle this.
The search engine had already begun to fight against low-quality content with the previous update, the Panda algorithm, and Penguin served to build on what Panda had already worked to achieve and provide a better framework to encourage more high-quality results.

When Google realised that there was a significant increase in content being manipulated to achieve higher rankings, it developed the Penguin update to step in. This manipulation included what is known as ‘black hat’ techniques in which quality of content is foregone in place of link cramming and keyword stuffingKeyword stuffing is a technique that attempts to give pages higher rankings in search engine result pages by inserting the same keywords over and over again., deemed its own form of spam.
Avoiding these techniques is essential for quality content. That’s why it’s essential to seek Search Engine Optimisation services to help develop quality content which includes natural links and organically placed keywords.
Regarding low-quality links, Google worked to better understand links and how to process them with its Penguin update, to only supply natural and authoritative results on its top-placed rankings. Manipulative and spammed content was therefore moved down in the rankings.
Penguin’s focus regarding link manipulation is based solely on the links which point back to a website in question. This update does not take into consideration the links which are included on the website itself.
Therefore, Google’s aim with the Google Penguin UpdateGoogle's Penguin algorithm update was designed to reduce rankings for sites that violate Google's webmaster guidelines for spammy links. 2018 was to ensure that all top-quality and authoritative content would be rewarded with a higher place in its search results.
The launch of Penguin actually went through several different updates during its development. While the initial impact was around 3% of English search engine queries, the update went a step further and had several updates between 2012 and 2016 to cause further impact. These updates would majorly influence the way businesses and SEO experts would understand search engine rankings and relevant content.
Following these updates, Penguin is now a fundamental part of Google algorithms.
Some of the updates which were made during Penguin’s progression include:
This initial update was more a refresh to what had originally been developed. It meant that those with low-quality content the first time round had the chance to recover if they had tidied up their links since the initial release, but it also meant that those who had been missed the first time had more chance of being caught by Penguin during this first refresh.
Penguin took its next refresh a step further but addressing international queries as well as those in English.
Weather report: Penguin data refresh coming today. 0.3% of English queries noticeably affected. Details: http://t.co/Esbi2ilX
— Matt Cutts (@mattcutts) October 5, 2012
Penguin 2.0 advanced during this time and developed how the algorithm impacted search results. This saw the update investigating more closely into website content, and to understand better how link spamming occurred to tackle it.
The next refresh, this affected around 1% of Google queries. It has also been acknowledged that this update would concentrate even more intensely on spam links and low-quality content, allowing Penguin to dive even deeper.
Penguin 2.1 launching today. Affects ~1% of searches to a noticeable degree. More info on Penguin: http://t.co/4YSh4sfZQj
— Matt Cutts (@mattcutts) October 4, 2013
Penguin here gave a chance for those impacted by previous refreshes to recover by refreshing its data yet again. With 3.0, Penguin sought to catch those who had continued to try and utilise spamming link practices.
The final update saw Penguin officially instated as part of Google’s core algorithm. With Google’s official support, the algorithm runs in real-time to continually be evaluating and analysing links to seek out quality content and eliminate negative linking practices.
The Penguin algorithm has two main focuses when it comes to sifting through content for Google. These two focuses are on unnatural link building, and keywordKeywords are the words and phrases that potential customers might search for to find your business. stuffing.
Regarding links, Google likes high-quality links from authoritative sources. With Penguin, this means that any links populated on low-quality sites or a wealth of backlinks gained from unrelated content will be penalised by the update. Penguin aims to eradicate unnatural and untrustworthy link systems, such as when businesses use alternative websites to promote themselves on an unreliable basis and gain more backlinks to their website.
Furthermore, Penguin works to understand the relevancy of all sites which have business backlinks on them. It will be able to understand why a website, including a backlink, has any relevancy at all to the business in question — and if not, it will be penalised.
Regarding keyword stuffing, Penguin knows when keywords are unnaturally overpopulating a page, and when they appear in an attempt to manipulate rank position. Google will be able to analyse unnatural repetitions of keywords in a phrase, for example, to process whether keywords have been suitably placed. Quality SEO services can assist in the best, the natural placement of keywords for those businesses which are unsure.

Before the Penguin update — and even alongside the Penguin update — Google maintains its own manual penalty system for any unhealthy practices when it comes to link building and keyword placement. Penguin has served to reinforce this. While Google’s manual system works to determine individual websites which are considered spam, the Penguin update provides a broader range by being applied to all websites across the board.
To best determine whether your rankings have been affected by the Penguin update, you can use analytics to view whether your rankings dropped significantly or were negatively impacted during the time of Penguin’s first release, or the subsequent updates mentioned above. This will take careful evaluation in under to first understand whether any other factors may have caused the dip in rankings, as it may not have been the Penguin update which was responsible.
If you are unsure whether your linking practices would be considered as spam-like by Google or Penguin, then you can seek guidance from an SEO service or b2b SEO agency to analyse your link-building methods and understand whether they would be deemed healthy or not.
If you do find that you have been affected by the Penguin update and that your rankings have suffered; as a result, the main task at hand will be to tidy up your linking system so that the next time Penguin’s update and Google’s analysis crawls through your site and relevant content, it will be able to reconsider its previous penalty if it can see that you have more positively tidied up your linking and keyword system. You can consult with an SEO expert to gain assistance in tidying up your link building and recovery from the Penguin update.
Steps to take include:
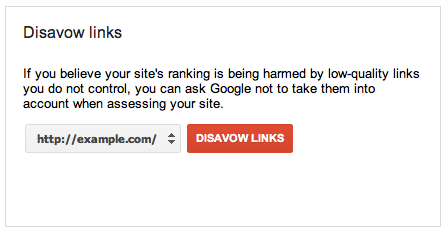
Building up authoritative and high-quality links can seem like a tough task for many businesses which aren’t familiar with link building or with how Google and the Penguin Algorithm Update choose to read them.
As a professional search engine marketing agency, Click Intelligence knows how to develop authoritative links and ensure that link building is done naturally to push your business to the top of the ranks. If you’re looking for a high-quality SEO agency to assist with your initial link building, or to help you recover from the Penguin update, we can help.

Seasonality can have a huge effect on the success of your business. It is imperative to have a strong digital marketing campaign during periods of high consumer demand.
Link Building or Managed SEO which is right for me?
Ah, 2021 – the year of volatile Google algorithm updates that shook marketers from within and left website owners scratching…