The December 2025 Google Core Update Is Complete: What Does It All Mean?
When a Google core update is being rolled out, digital marketers everywhere eagerly wait to…
Most people with websites know what the Google core web vitals are by this point. They were developed just a few years ago in 2021, when Google released their new way of ranking websites based on user experience. At the time, those core web vitals included LCP, FID, and CLS, but that changed a little in March 2024, when Google introduced the core vital INP.
So, what do all these acronyms mean? For those eager to appease Google and, in turn, run a successful website, understanding what these core web vitals are is crucial (of course, you can also use high-quality SEO services to manage the tricky parts for you).
It’s all about improving user experience and boosting your Google ranking. If you’re a website owner, you want to appeal to both Google and any user who clicks on your site. As the name would suggest, core web vitals refer to the absolutes of website metrics – three main metrics of your website that give a particular score, painting a picture of how well the website runs for users. The better the score, the better your website runs, and everyone knows user experience matters most!
LCP, INP, and CLS (and, previously, FID) are the core web vital metrics, and each is essential to know about in its own right. A technical SEO audit can help cover these metrics, including the technical parts of making your website rank higher on search engines.
Itching to boost your ranking? You can learn more about on page SEO to find out how it might benefit your business.
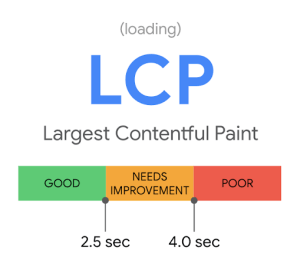
Let’s discuss LCP first, which stands for Largest Contentful Paint. So, what is LCP? LCP is a core web vital that measures the biggest piece of visual content on the webpage – for example, that might mean a large image at the top of the page. This one’s all about speed, measuring how long it takes to visually appear on the screen. An LCP speed of 4.0 seconds or below is poor, between 2.5 and 4.0 seconds falls under ‘needs improvement’, and a speed of 2.5 seconds or faster is considered good. Naturally, to avoid an LCP issue, you’ll want to fall under the ‘good’ category.
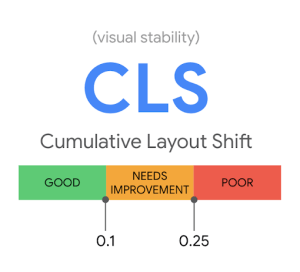
CLS – which stands for Cumulative Layout Shift – is another metric measured by Google and part of the core Google web vitals. Unlike LCP, this one doesn’t focus so much on speed. Instead, it measures the visuals that move around on the page when a user is on there. The more visual movement, the more annoying it can be for the user, creating a poorer experience. The better
web pages have far more stability, and this will give you a better CLS score, which is anything above 0.1. Between 0.25 and 0.1 falls under ‘needs improvement’, and anything under 0.25 is ‘poor’.
If you’re interested, you can read more about our SEO Consultancy Services.
When the core web vitals were first introduced in 2021, they consisted of LCP, CLS, and FID, but FID has since been replaced with INP (which we will go into below). However, it’s still worth knowing what FID was and what it measured, as well as why it may have been replaced.
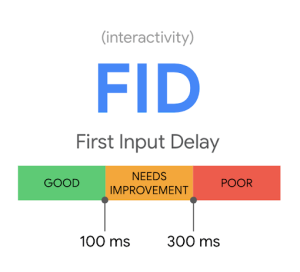
FID – which stands for First Input Delay – was a core ranking metric that measured the time between the user’s first interaction and the website’s initial response. The faster, the better. When measured, a good FID score was anything above 100ms, and a poor FID score was under 300ms.
Google Web Vitals introduced INP as a replacement for FID in March 2024. INP stands for Interaction to Next Paint, a metric that assesses how quickly a website responds to the user’s interactions. Instead of focusing on the single metric of the first user interaction – which is what FID measures – it’s more of an overall measurement that takes all the user interactions into account while they are on a page.
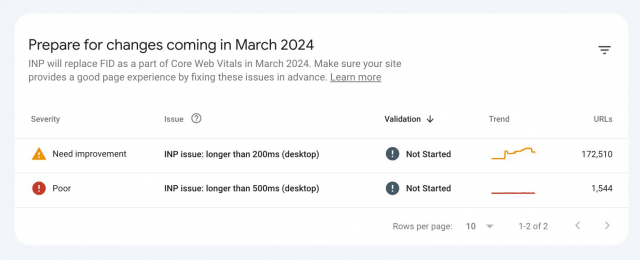
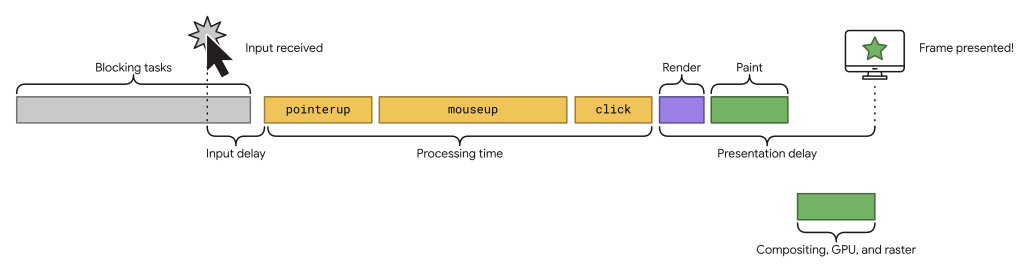
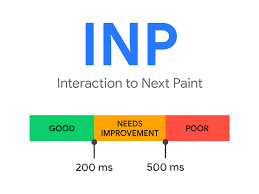
Google scores the INP by the longest metric taken. A poor score is over 500ms, a score that needs improvement is between 200-500ms, and a good score is below 200ms.
Get an SEO audit here and see how your website is doing, so you have a better picture of your website’s performance and what you can do to improve it.
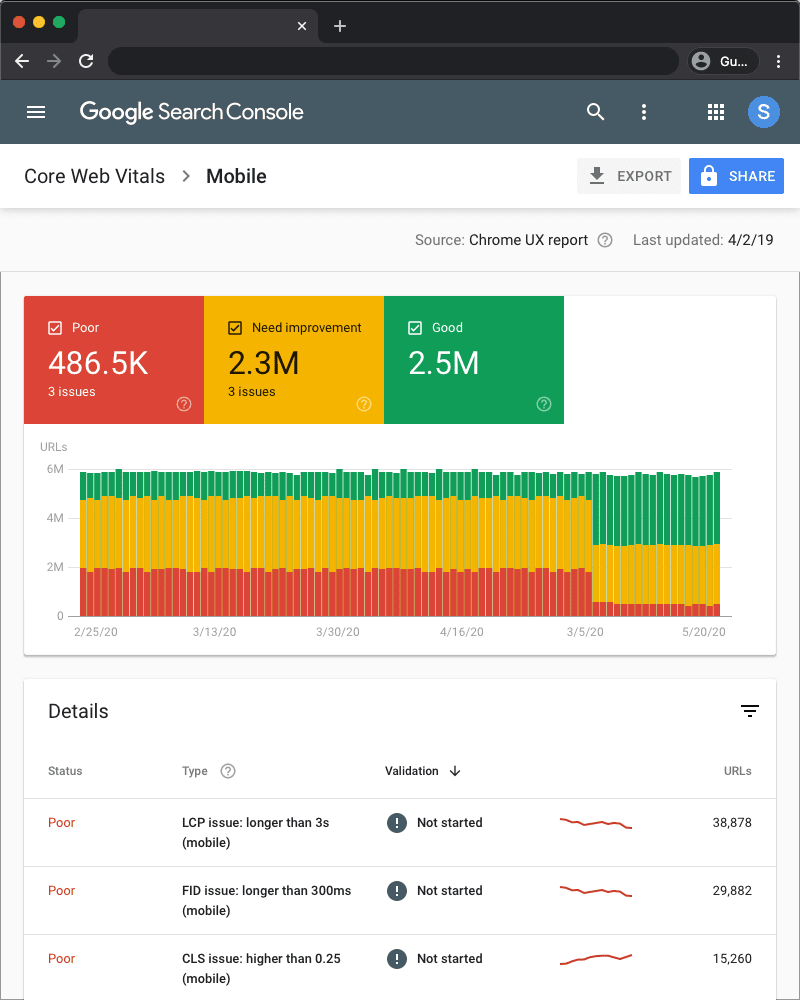
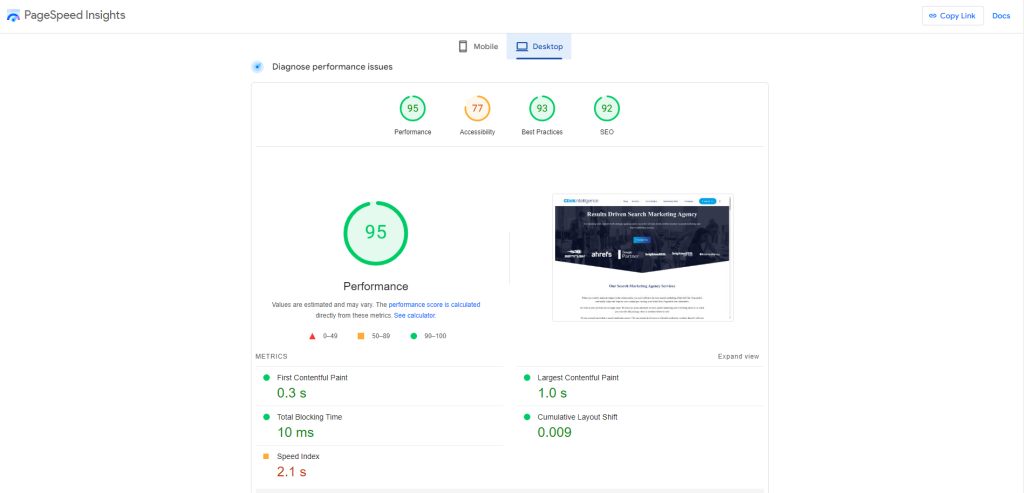
The first step to optimizing web core vitals is to understand the core vitals definition and know how to measure them. The good news is there are plenty of excellent tools to measure your core web vitals, including Lighthouse, Google Search Console, and PageSpeedThe Google PageSpeed Insights Tool is a free and easy-to-use tool that provides webmasters with a score (from 0 to 100) that reflects the performance of their site on mobile devices. Insights. Once you know your metrics, you’ll be able to see where your website may be failing and make the adjustments as necessary. A good SEO management strategy should encompass this, helping you tackle the core web vitals and ensure your website consistently produces good scores.

It can be challenging to navigate the ever-evolving factors that affect your website’s performance and overall ranking. It can feel like a dark art that you’ll just never get the hang of. That’s why so many of the best-performing websites use SEO services, taking advantage of the expertise out there rather than trying to go it alone. At Click Intelligence, we offer a wide range of SEO services, including international SEO, enterprise SEO, and white label SEO, to help you tackle all your search engine needs. We understand that a small business’s SEO strategy should be different from an enterprise, and we tailor our services to meet your specific needs.
Hopefully, we have given you a simple core web vitals definition and made the metrics like Google CLS and INP much clearer. If you have any questions about Google core web vitals or search engine optimisation as a whole, get in touch with the Click Intelligence team today!
It's clear that a new management approach can do wonders for your company, and one of the most cutting-edge and…
Download our free Millionaires SEO Guide Today!
If Google's latest Web Core Vitals update has caused havoc to your SEO results, find your solution in our latest in-depth ebook.