Search has significantly evolved since the early days of manual directories and early crawlers. In recent years, keyword-driven search engines were everything, but that has now made way for AI-powered generative engines like Google AI Overviews, AI Search, and LLMs. As a result of this, evolving SEO practices are necessary, which is what our SEO services offer!
If you’re eager for content discoverability, you need to understand the difference between SEO and GEO. SEO (search engine optimisation) is the practice of improving a website’s search visibility by ranking higher on search engines. On the other hand, GEO (generative engine optimisation) is about making websites more visible to AI-driven search engines.
With our generative engine optimisation guide, learn more about why this shift matters for future-proofing your content and keeping your rankings.
What Is Classic SEO?
Classic SEO focuses specifically on SERP rankings, with traditional SEO methods including things like backlinks, keyword optimisation, metadata, and on-page SEO.
Classic SEO focuses on search engine indexing and rankings based on signals such as authority, content quality, and structure. Of course, it has evolved within itself over the years, with Google frequently changing its ranking factors.
What Is Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimisation, or GEO SEO, is a type of AI search optimisation with the main goal being featuring in LLM Search, Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT responses, and Perplexity. AI search often leads to a zero-click search, which means users receive answers without actually clicking on a link to a website.
GEO prioritizes structured content, credibility, and content that can be easily summarized and cited by AI. For example, using structured data for web pages is a way of allowing AI-driven search engines to read and understand a page’s content better. As a result, that could mean a better chance of featuring in AI summaries.
Key Differences Between SEO and GEO
So, what’s the difference between classic and generative SEO? Let’s compare SEO vs GEO to find out.
Classic SEO
SERP ranking: SERP rankings appeal to search engine algorithms. This dictates the position of a website on results pages for particular keywords.
CTR: Click-through rate is all about how many people click on a web page in SERPs and is an essential metric for SEO performance.
Crawlability: SEO crawlability refers to search engine crawlers like Googlebot and how well they are able to navigate a website page. If done right, the crawler will index the page and help it rank higher.
GEO
Entity recognition: Entity SEO refers to the process of identifying entities within content, for example, an organization, location, time, or person.
Trust signals: GEO focuses on a range of trust signals, specifically E-E-A-T (expertise, experience, authoritativeness, trustworthiness). This is one of the ways that GEO and SEO have an overlap.
Citation potential: Citation-based ranking matters for GEO and AI-driven results. This is the likelihood of another publication linking to your own web page, which helps AI understand the context of the page.
Here are some of the clearest differences between SEO and GEO.
Ranking mechanisms: Ranking mechanisms for SEO include things like keywords, backlinks, content quality, and user experience. On the other hand, ranking mechanisms for GEO include clarity, conciseness, natural language, structured data, and authority.
User intent targeting: SEO and GEO target different user intents. SEO is about matching content explicitly to what the searcher is looking for, focusing more on the why (informational, navigational, and transactional, for example), and it often targets a website’s users through keyword research. GEO is different, as it targets users who want easily digestible answers.
Role of schema: Schema markup plays a vital role in GEO. GEO is about helping AI-driven search engines understand web pages, and schema helps with that through structured data. SEO focuses more on users.
Content formatting: Traditional content formatting for SEO includes key elements like keyword integration, clear headings, meta descriptions, and bullet points. GEO is more about AI summarization, so the key elements include structured data, scannable paragraphs, and concise answers.
A good content strategy and content writing will incorporate content that appeals to both sides, depending on your target audience.
On-Page SEO vs On-Page GEO Optimisation
There are different techniques used for on page SEO vs GEO/AI SEO
SEO
On-page SEO always focuses on the user first. It is about making the content in-depth yet still readable, while also appealing to search engine crawlers that index the page. Some techniques for this include keyword placement, internal linking, and title tags.
GEO
For on-page GEO, well-structured content and answer-first formatting is key. Schema markup is important for readability for LLMs. Content optimisation for AI involves easily understandable, clear, and contextual content. For this, bullet points, concise answers, and structured sections make sense.
Off-Page SEO vs Off-Page GEO Signals
Off-page GEO and SEO also differ.
SEO
SEO focuses more on acquiring backlinks, authority building, and anchor text. For example, a good SEO strategy will often include digital PR and blogger outreach to acquire more backlinks and gain credibility.
GEO
When it comes to off-page techniques for GEO purposes, it often includes digital credibility, external validation, brand citations, expert mentions, and SameAs schema. Link building for AI still matters, too, as it works as an E-E-A-T signal.
It’s important to note that off-site entity SEO is also important; it’s just that entities matter more in AI-driven searches.
Role of Schema Markup in GEO vs Classic SEO
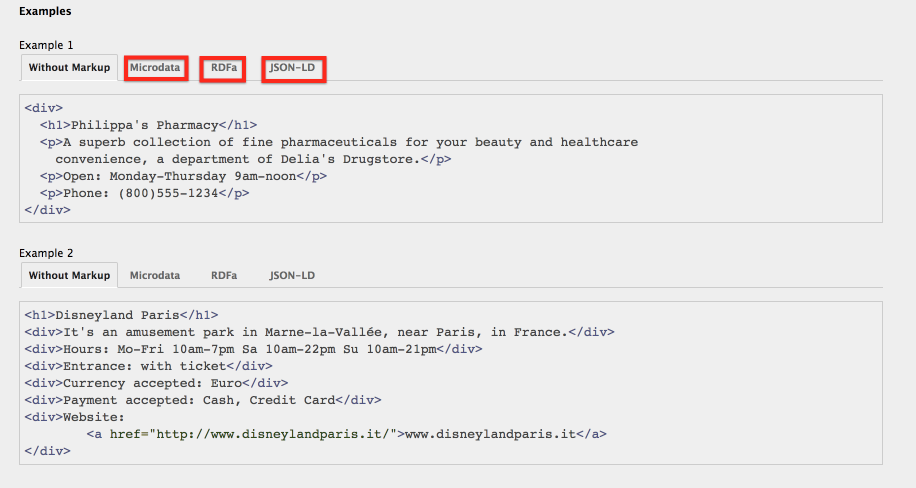
Schema markup refers to the knowledge extraction of structured data by search engines or AI-driven engines. Schema markups can be created with a language like JSON-LD.
Structured data is helpful for both SEO and GEO, but it plays a bigger role in AI-driven summaries.
Schema SEO: For classic SEO, the best schema markups include Article, Product, and Organization.
Schema for GEO: Schema for GEO improves LLM readability of a web page. The best schema markups for this purpose include FAQPage, HowTo, WebPage, Speakable, Author, and Review.
If you want to improve schema for GEO or SEO, it helps to validate the schema with Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema.org tools.
How to Optimize Content for GEO Without Abandoning Classic SEO
Do you want to optimize for GEO and SEO? If so, you need a dual-purpose content strategy, also known as a hybrid SEO strategy – one that offers a mix of entity optimisation, semantic SEO, and trust-first content.
To keep up with your SEO efforts, maintain keyword research, as this will still help you with ranking higher in search engines. However, at the same time, prioritize semantic depth, offering AI engines a deeper understanding of the context of the content.
Adding schema markup is a no-brainer that can actually help both SEO and GEO, so it works in unison. You can also add on structured Q&A formats to your content, perhaps at the end, as this will appeal to AI while still allowing your content to be useful for real readers.
For increased authority – which helps both SEO and GEO simultaneously – you can also establish author entities better and link to high-authority sources. To help with this, we have a dedicated link building service.
Tools and Platforms That Support GEO Optimisation
Are you looking for GEO SEO tools and generative engine optimisation platforms? Whether you’re interested in entity tracking, tracking LLM traffic, structured data tools, or Google AI metrics, there’s a tool here for you:
- Schema markup generators: Merkle, RankRanger.
- Entity research tools: Kalicube, InLinks.
- Click tracking in AI: GA4 referrers, LLM dashboards, Click Insights.
- Google Search Console insights for featured/snippet views.

Future of Search: Why GEO Is the Next Frontier
Understanding next-gen search engines and the general future of SEO (and GEO future) is important, as it means adapting your methods and staying visible online. AI overviews and conversational search are already having a massive impact on how users search for and interact with content.
It is clear that citation-driven rankings and zero-click SEO are becoming more popular, and the growth of LLM search engines will only increase. Over time, blue-link-only strategies will diminish in value.
Preparing for GEO While Retaining SEO Value
Ready for the SEO to GEO transition? Here’s a GEO SEO checklist to ensure you stay on top:
- Create a schema markup.
- Ensure entity consistency across all pages and platforms.
- Create well-structured content that directly answers questions.
- Build author and brand credibility signals
- Focus on AI-friendly internal linking.
Are you looking for more search strategy or optimisation tips? Perhaps you want an AI-driven content plan. If so, you’re in the right place. At Click Intelligence, we have a range of SEO services and resources to suit your strategy. Here are more resources:
Click Insights, SEO reporting software